Wireless technology has become an invisible part of our lives — from streaming music through Bluetooth earbuds to browsing the internet on Wi-Fi. Yet, while both use radio waves to connect devices without cables, they serve very different purposes.
Let’s break down the difference between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, how each works, and which one suits your needs better.
What is Bluetooth Technology?
Bluetooth is a short-range wireless communication technology designed for direct device-to-device connections. It works within about 10 meters (30 feet) and uses low energy to send data, making it perfect for connecting small gadgets.
Bluetooth uses the 2.4 GHz frequency band and operates by creating a “piconet,” a small network where one device acts as the master and others as slaves. For example, when your phone connects to wireless headphones, Bluetooth pairs them so that they remember each other next time.
Shop wireless neckbands designed for comfort and powerful sound that let you enjoy your favorite tracks calls and workouts with flexibility and style every day.
Common Bluetooth Uses
- Wireless audio devices like headphones, earbuds, and speakers
- Smartwatches and fitness trackers
- Keyboards, mice, and game controllers
- IoT devices and beacons for smart homes
Its low power consumption makes Bluetooth ideal for portable devices that run on small batteries.
What is Wi-Fi Technology?
Wi-Fi, short for Wireless Fidelity, is a networking technology that connects multiple devices to the internet or a local area network (LAN). It also operates on radio frequencies — mainly 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and now 6 GHz (Wi-Fi 6E) — but unlike Bluetooth, Wi-Fi covers a much larger area and delivers far higher speeds.
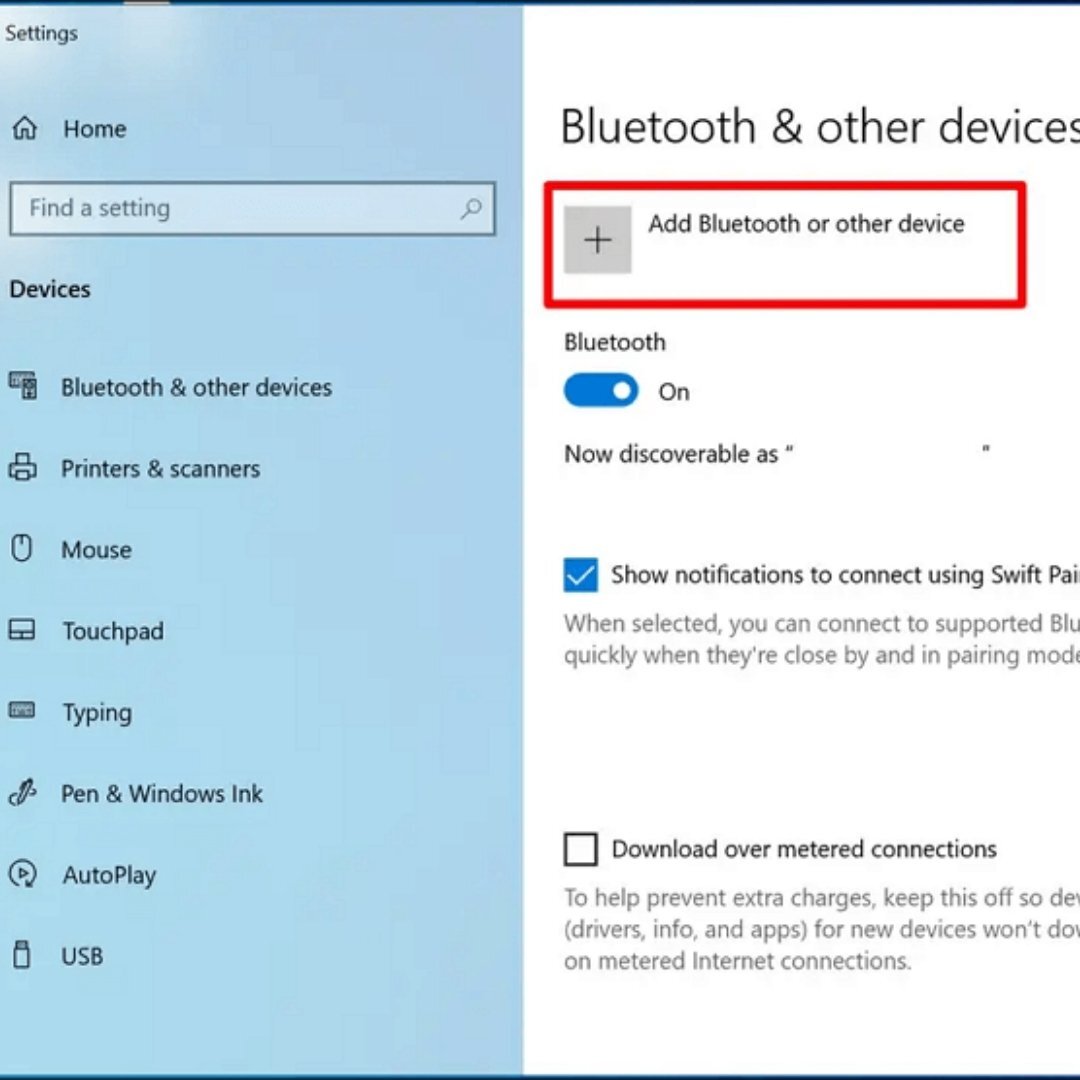
Wi-Fi networks use routers and access points to broadcast signals. Devices within range can connect by entering a password or security key.
Shop true wireless earbuds with instant pairing lightweight design and powerful bass that make them your go to choice for music and lifestyle use.
Common Wi-Fi Uses
- Internet access for laptops, smartphones, and smart TVs
- Streaming movies, online gaming, and cloud storage
- Office and home network connections
- Public hotspots in cafes, airports, and hotels
Wi-Fi’s primary goal is internet sharing, whereas Bluetooth focuses on direct communication between devices.
Key Differences Between Bluetooth and Wi-Fi
|
Primary Purpose
|
Short-range device-to-device connection | Internet access and local networking |
|
Range
|
Up to 10–30 meters | Up to 100 meters or more (indoors and outdoors) |
|
Speed
|
Up to 3 Mbps (Bluetooth 5.0) | Up to 9.6 Gbps (Wi-Fi 6) |
|
Power Consumption
|
Low | Higher |
|
Security
|
128-bit encryption | WPA2/WPA3 encryption (more secure) |
|
Setup Complexity
|
Simple pairing | Requires router and configuration |
|
Network Structure
|
Master-slave (piconet) | Client-server (router-based) |
|
Frequency Band
|
2.4 GHz | 2.4 GHz, 5 GHz, and 6 GHz |
While Bluetooth connects two or a few devices, Wi-Fi connects many devices simultaneously within a larger network.
Shop wireless headphones with high resolution sound noise isolation and cushioned comfort built for music movies and gaming with ultimate clarity all day.
Applications of Bluetooth And Wi-Fi
Bluetooth Applications
- Wireless Audio: Connect headphones, speakers, and car systems without cables.
- Wearables: Used in fitness trackers and smartwatches for data syncing.
- IoT Devices: Enables communication in smart homes and health monitoring systems.
- File Sharing: Transfers small files between nearby devices.
Wi-Fi Applications
- Internet Access: Connects devices to the web in homes and offices.
- Streaming: Powers Netflix, YouTube, and online gaming.
- Smart Homes: Integrates smart TVs, security cameras, and home assistants.
- Business Connectivity: Supports cloud storage, conferencing, and remote work setups.
Bluetooth shines in personal and portable connections, while Wi-Fi dominates broadband and networking scenarios.
Shop Bluetooth speakers with powerful bass crystal clear vocals and portable designs that keep your music alive whether indoors or outdoors all day long.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi
Bluetooth
Advantages:
- Low power consumption
- Easy and fast pairing
- Cost-effective technology
- Works without an internet connection
Disadvantages:
- Limited range and speed
- Not ideal for large data transfers
- Fewer simultaneous connections
Wi-Fi
Advantages:
- Long-range coverage
- High-speed data transfer
- Supports multiple devices
- Secure with advanced encryption
Disadvantages:
- Consumes more power
- Requires setup and a router
- Can face interference from other devices
Each technology excels in its own way — Bluetooth focuses on efficiency and simplicity, while Wi-Fi emphasizes speed and connectivity.
Shop power banks designed for fast charging long battery life and portability ensuring your devices stay powered during work travel or daily use.
Future of Bluetooth and Wi-Fi
Both technologies continue to evolve to meet the growing demand for faster, smarter, and more efficient wireless communication.
The Future of Bluetooth
- Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE): Ultra-efficient for IoT devices.
- LE Audio: Better sound quality and synchronized audio sharing.
- Improved Security: Newer encryption protocols for safer data exchange.
The Future of Wi-Fi
- Wi-Fi 6E and 7: Faster speeds, lower latency, and improved performance.
- Smart Environments: Wi-Fi networks powering entire buildings or cities.
- Seamless Device Integration: Smarter switching between mobile and Wi-Fi networks.
Together, these advances will keep both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi at the core of future connectivity — one for personal communication, the other for global networking.
Conclusion
Both Bluetooth and Wi-Fi are vital for modern wireless communication, but serve distinct roles. Bluetooth connects devices over short distances using minimal power, making it perfect for accessories and IoT gadgets. Wi-Fi, meanwhile, provides high-speed internet access across larger areas, powering homes, offices, and public spaces.
Knowing their differences helps you choose the right technology — Bluetooth for personal connectivity, Wi-Fi for network access. As both continue to advance, they will remain the twin pillars of our connected world.
Shop smart watches combining fitness tracking style and advanced features that help you stay connected healthy and active every day with ease.
FAQs About the Difference Between Bluetooth And Wi-Fi
1. Which is faster, Bluetooth or Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi is much faster, offering speeds up to several gigabits per second, while Bluetooth is limited to a few megabits.
2. Can Bluetooth connect to the internet?
No, Bluetooth only connects devices directly; it doesn’t provide internet access like Wi-Fi.
3. Which uses more power, Bluetooth or Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi consumes more power, while Bluetooth is optimized for low energy use.
4. Which is more secure, Bluetooth or Wi-Fi?
Wi-Fi offers stronger security with WPA2 and WPA3 encryption compared to Bluetooth’s basic encryption.
5. Can Bluetooth and Wi-Fi work together?
Yes, modern devices can use both simultaneously without interference.